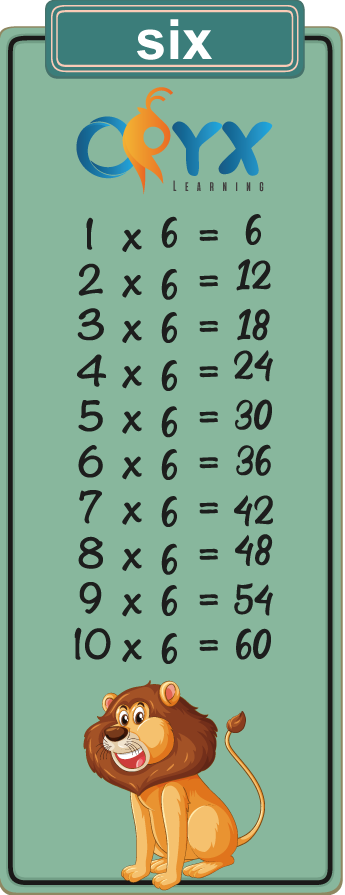6 Times table
Concept
Table of 6 shows the values we get when the number six is multiplied by other whole numbers. Multiplication tables, once mastered can become second nature to a student and will become fundamental in day to day life. A fun fact we learn from the 6 times table that 6 is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number. The repeated addition of 6 is the multiplication table of 6.
Multiplication Table of 6
Learning the multiplication table of 6 is an essential skill for the problems based upon fractions, decimals, and percentages. It helps in solving real-life problems quickly when the students are outside their classrooms and make students understand the sequences and patterns followed by the multiples of 6.
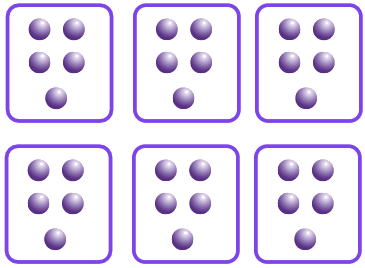
You can view multiplication as telling you how many groups of something you have. So, when you have multiplication of 6, you will have six groups of something. For example, 6 x 4 tells you that you have six groups of 4. To find the answer, you add your groups together. So, 6 x 4 turns into 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4, which turns into 24. So, 6 x 4 is equal to 24.
6 Times Table up to 10
The 6 multiplication table is all about adding the number six times.
6 Times Table Chart
Tips for 6 Times Table
1. Multiples of 6 are both multiples of 2 and multiples of 3.
6 times 2 = 12 . We observe that 12 is a multiple of both 2 and 3.
6 times 3 = 18. 18 is a multiple of both 2 and 3.
2. When we multiply an even number by 6, the last digit is the same. That is, 6 × 4 = 24 , 6 × 6 = 36 , 6 x 8 = 48
Rules
When a number is multiplied by 6, the answer is six times the number. Add the number 6 times.
You can also find the product with the help of skip counting. Skip count by 6’s like 6, 12, 18, 24 . . . and so on.
Example
Multiply.
6 x 5
Solution
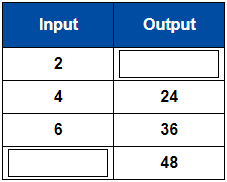
Practice 6 Times table

Multiplication – you take one number and add it together a number of times.
Product – When we multiply two numbers, the answer we get is called ‘product’.
Multiplicand – the number of objects in each group.
Multiplier – the number of equal groups is called ‘multiplier’.