Linear vs Nonlinear Functions
Concept
A linear function is a function whose graph is a straight line. For example, y = 4x – 5 represents a straight line on a coordinate plane and hence it represents a linear function. Since y can be replaced with f(x), this function can be written as f(x) = 4x – 5.
A nonlinear function is basically the opposite of a linear function. This gives that the graph of a nonlinear function is not a line, and we can determine whether a function, in tabular form, is nonlinear by observing that the jump in y varies for each unit of change in x.
Rules
How to determine a linear/nonlinear function through tables:
1. Calculate the rate of change (slope) for each ordered pair.
2. If the rate of change is constant, the table represents a linear function.
3. If the rate of change is not constant, the table represents a nonlinear function.
How to determine a linear/nonlinear function through tables and graphs:
1. Plot the ordered pairs.
2. The points have a linear relationship if a straight line passes through all points.
3. The points have a nonlinear relationship if no straight line passes through all points.
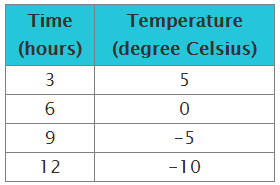
Example
Solution
The temperature decreases 5 degrees for every 3-hour change in time. That is a constant rate of change, indicating that the function is linear.
Practice Linear vs Nonlinear Functions

Linear: To fall in a straight line.
Function: A relation in which every member of the domain (input value) is paired with exactly one member of the range (output value).
Linear Function: A function in which the graph of the solutions forms a straight line.
Function Table: A table organizing the domain, rule, and range of a function.
Nonlinear functions are functions whose rates of change are not constant. A nonlinear function has a graph that is not a straight line.
Rate of Change – ratio of the “vertical change” to the “horizontal change” between (any) two distinct points on a line. It is also called the slope.
Related Skills
Algebra Functions
Slope
Direct Variation
Quadratic Functions
Qualitative Graphs