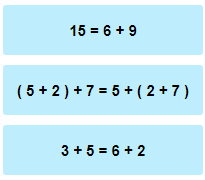Properties of Addition
Concept
The addition is a process of adding two or more items together. In math, addition is the method of calculating the total of two or more numbers to know the sum of the numbers. It is a primary arithmetic operation.
Rules
While performing addition we use the basic properties listed below:
Commutative Property: The commutative property of addition says that the order in which we add the addends does not change the sum.
The sum of two or more addends will be the same irrespective of the order of the addends. For example, 5 + 3 = 3 + 5 = 8
Associative Property: The associative property of addition is a rule that states that while adding three or more numbers, we can group them in any combination, the sum that we get remains the same irrespective of the manner in which they are grouped. In this case, grouping refers to the placement of brackets.
The sum of three or more addends will be the same irrespective of the grouping or order of the addends. For example, (6 + 4) + 5 = 6 + (4 + 5)
Additive Identity Property: If we add 0 to any number, the sum remains the actual number. The addition of the whole number 0 to any other number does not change the value of the sum. For example, 0 + 8 = 8.
Example
Which property of addition does this equation show?
14.12 + (9.5 + 7.3) = (14.12 + 9.5) + 7.3
Solution
Associative property
When adding 3 numbers, grouping does not change the sum.
Practice Properties of Addition

The addition is an operation used in math to add numbers.
Commutative property of addition: The order of the numbers is changed, but the sum does not change.
Associative property of addition: When adding 3 numbers, changing the grouping does not change the sum.
Identity property of addition: When adding zero to any number, it equals the number itself.