Subtracting Algebraic Expressions Using Algebra Tiles
Concept
In mathematics, just like we subtract many numbers as we can and find the difference, we subtract two or many algebraic expressions too. However, for the subtraction of algebraic expressions, we combine all the like terms and then subtract them.
Like terms are the terms that have the same power for the same variables. In like terms, one can only change the numerical coefficient. Terms that have different variables or the same variables raised to different powers are known as, unlike terms.
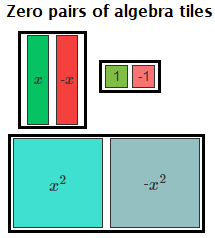
When modeling subtraction of algebraic expressions, we can use algebra tiles to represent these expressions. One colored tile represents a positive number and another colored tile represents a negative number. A zero pair is the pair of the positive and negative form of the same number/variable.
Rules
1. Model the first linear expression.
2. Add or remove zero pairs as needed to subtract.
3. Write a linear expression for the remaining tiles.
Example
Subtract using algebra tiles.
(3x – 2 ) – (2x + 1)
Solution
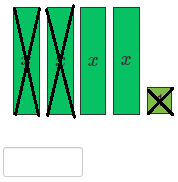
Model the first linear expression.
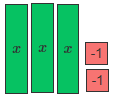
Since there are three x-tiles, remove two x-tiles.
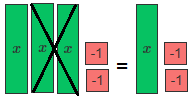
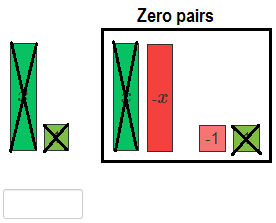
We need to remove 1 positive 1-tile, but there are only two negative 1-tiles. Add a zero pair of 1-tiles. Then remove one positive 1-tile.
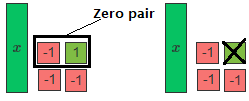
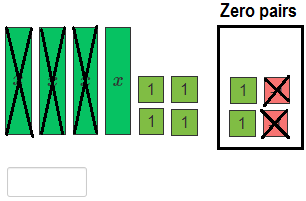
4. Write a linear expression for the remaining tiles.
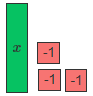
(3x – 2 ) – (2x + 1) = x – 3
Practice Subtracting Algebraic Expressions Using Algebra Tiles

Algebra tiles – mathematical manipulatives that allow students to better understand ways of algebraic thinking and the concepts of algebra.
Linear Expression – an algebraic expression in which the variable is raised to the first power, and variables are not multiplied or divided.
Term – either a single number or variable, or numbers and variables multiplied together. Terms are separated by + or − signs.
Like terms – Terms that have the same power for the same variables. In like terms, one can only change the numerical coefficient.
Unlike terms – Terms that have different variables or the same variables raised to different powers.
Distributive Property – to multiply a sum or difference by a number, multiply each term inside the parenthesis by the number outside the parenthesis.
Constant – a term without a variable.
Variable – In algebra, a symbol (usually a letter) standing in for an unknown numerical value in an equation or expression.
Coefficient – is an integer that is multiplied with the variable of a single term or the terms of a polynomial.
Pre-requisite Skills
Evaluate Variable Expressions-addition and subtraction
Evaluate Expressions (Multiplication and Division)
Solve Algebraic Equations – Addition and Subtraction
Solve Algebraic Equations – Multiplication and Division
Evaluate Algebraic Expressions
Write Algebraic Expressions
The Distributive Property
Simplifying Complex Algebraic Expressions
Add Linear Expressions