What are Measures of Central Tendency
Concept
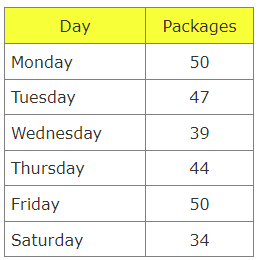
Measures of central tendency describe a set of data by identifying the central position in the data set as a single representative value. There are generally three measures of central tendency, commonly used in statistics- mean, median, and mode. Mean is the most common measure of central tendency used to describe a data set.
Mean- Sum of all observations divided by the total number of observations.
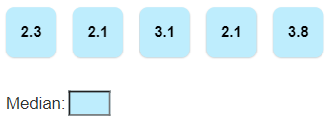
Median- The middle or central value in an ordered set.
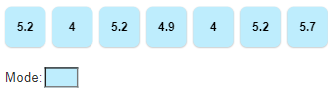
Mode- The most frequently occurring value in a data set.
Rules
Mean:
To find the mean of a data set, add up all the numbers, then divide by how many numbers there are.
Mean =
Median:
Arrange the numbers in order from the least to the greatest.
Find the middle number of the set. If there is an even number of items in the data set, compute the median by finding the mean of the two middle numbers.
Mode:
To find the mode, arrange the numbers in order. Then count how many there are of each number. A number that appears most often is the mode.
Example
Solution
Practice What are Measures of Central Tendency

The central tendency is defined as the statistical measure that can be used to represent the entire distribution or a dataset using a single value called a measure of central tendency.
Mean – Sum of all observations divided by the total number of observations.
Median – The middle or central value in an ordered set.
Mode – The most frequently occurring value in a data set.