Terminating and Repeating Decimals
Concept
The decimal representation of a rational number is converting a rational number into a decimal number that has the same mathematical value as the rational number. A rational number can be represented as a decimal number with the help of the long division method. We divide the given rational number in the long division form and the quotient which we get is the decimal representation of the rational number. A rational number can have two types of decimal representations (expansions):
Terminating
Non-terminating but repeating
While dividing a number by the long division method, if we get zero as the remainder, the decimal expansion of such a number is called terminating. And while dividing a number, if the decimal expansion continues and the remainder does not become zero, it is called non-terminating or repeating. The decimal form of a fraction usually represented by a bar over the repeating numbers.
Rules
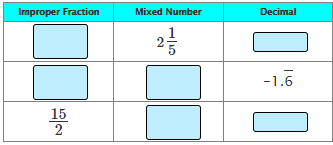
1. If the number is a mixed number, convert it into an improper fraction.
2. Just divide the numerator by the denominator. If you end up with a remainder of 0 , then you have a terminating decimal. Otherwise, the remainders will begin to repeat after some point, and you have a repeating decimal.
3. Determine which answers are repeating decimals and put a bar over the repeating numbers in the decimal.
Example
Write the number as a decimal. Use bar notation if necessary.
Solution
1. If the number is a mixed number, convert it into an improper fraction.
2. Just divide the numerator by the denominator. If you end up with a remainder of 0 , then you have a terminating decimal. Otherwise, the remainders will begin to repeat after some point, and you have a repeating decimal.
3. The answer is a repeating decimal. Put a bar over the repeating number in the decimal.
Practice Terminating and Repeating Decimals

Terminating Decimal– a decimal which can be expressed in a finite number of figures or for which all figures to the right of some place are zero.
Repeating Decimal – a decimal in which after a certain point a particular digit or sequence of digits repeats itself indefinitely.